Reserve Bank of Australia Annual Report – 1976 Banking, Issue and Other Operations
The banking, note issue, and other operational services provided by the Bank absorb the majority of its staff in the capital cities and at the Note Issue Department in Melbourne.
Banker to Governments
The Reserve Bank is banker to the Commonwealth Government, the Governments of four of the States, and the Administration of the Northern Territory. In this capacity the Bank processed approximately 100 million cheques during 1975/6, a little over 20 per cent more than in the previous twelve months. The majority of the cheques drawn on the Bank are for regular welfare payments by the Commonwealth Government. A major contribution to the increase in cheque volumes came from the issue of Medibank cheques by the Health Insurance Commission, which began operations on 1 July 1975.
On behalf of the Commonwealth Government, the Bank maintains inscribed stock registries at each of its branches. These registries service the major proportion of government debt; they handle cash and conversion loans together with the continuing issue and redemption of Special/Savings Bonds and Treasury notes. The numerous subscriptions to the new Australian Savings Bond in January brought a sharply increased workload to registries. In a little over two months, 185,000 applications were received; this was more than double the number of Bond applications processed by the registries in most years in the past decade.
The face value of the government debt managed by the Bank increased by $3,024 million over the year to $16,580 million. The main components of this debt were Australian Savings Bonds $1,188 million, Special Bonds $909 million, Treasury Bills $850 million, Treasury notes $456 million and other marketable Commonwealth Government Securities $12,703 million.
The Bank also conducts registries for some semi-governmental authorities at Brisbane and for the Government of Fiji at Sydney and Melbourne; a new registry was established at Sydney during the year for the Government of Papua New Guinea to service its Australian currency loan obligations.
Rural Credits Department
The Rural Credits Department of the Bank continued to provide seasonal finance to assist the marketing, processing or manufacture of primary produce. At 30 June 1976 outstanding advances totalled $181 million, compared with $203 million twelve months earlier; of the latest total, advances to marketing boards accounted for $98 million and to co-operatives $83 million. As is usual, the level of advances fluctuated markedly during the year; from as low as $145 million in November 1975 to a peak of $494 million ($404 million for marketing boards) in March 1976. In 1974/5 the range of fluctuation was from $100 million to $405 million.
Finance for the marketing of wheat remained the major influence on lending. From the 1975/6 harvest the Australian Wheat Board received 11.2 million tonnes, 0.5 million tonnes higher than in the previous season. The demand for wheat remained firm and most of the exportable surplus has been sold or committed. For dairy products, the peak debt was lower than last year but the average level of advances throughout the year was higher. Advances for coarse grains reached a much higher level than last year but were quickly reduced in a buoyant market. Advances for other commodities followed mainly the pattern of the previous season.
Interest rates charged on advances remained unchanged at the range of 9.5/10.0 per cent per annum.
Note Issue
At the end of 1975/6 the value of Australian notes on issue was $2,921 million, 15 per cent higher than twelve months earlier; this compares with a rise of 18 per cent in the previous twelve months and 22 per cent over 1973/4. As usual the peak circulation, $3,325 million, occurred over the Christmas period.
Following a dual currency period, Australian notes ceased to be legal tender in Papua New Guinea at the end of 1975. Between April and December, ten million Australian notes with a face value of $25 million were withdrawn from circulation and replaced by new PNG currency, of which the major unit is the “kina”; this changeover mostly took place in the closing months of 1974/5.
18 Australian Notes on Issue
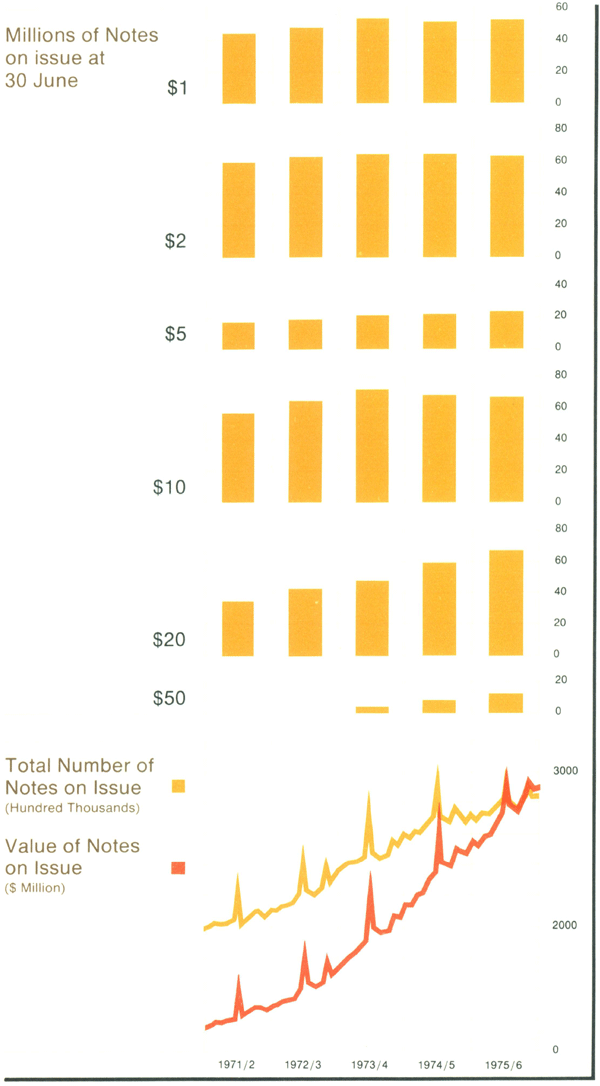
The tendency for a higher proportion of the value of Australian notes issued to be in larger denominations has continued. By the end of June, the value of $50 notes in circulation had increased since their first issue in October 1973 to 22 per cent of the value of all notes on issue. The share of the $20 note in the value of the total issue has remained constant, and that of each smaller denomination has fallen. However, the number of small denomination notes in circulation has, seasonal effects excluded, shown little net change; with rising price levels, these notes are used in more transactions. More intensive use of smaller denomination notes is a major factor in their shorter average life; the estimated average life of the $1 note is now as short as about seven months, compared with 2½ years for the $20 note. The increasingly active use of smaller denomination notes is bringing into sharper relief the need for improvement in techniques of culling out for destruction notes that are in sub-standard condition.
With the need to replace existing notes and to provide for increasing circulation, the Bank's Note Issue Department produced 371 million Australian notes in 1975/6; this was 32 per cent more than in the previous year. In addition, the Department produced a further 1,300 million pieces of security printing such as bonds, stamps and postal orders. Public demand for coin of all denominations has remained heavy and, notwithstanding an increase of 24 per cent in production by the Mint, the Bank had on occasions to ration issues of coin to banks.
During the year, the efficiency and security of existing methods of distribution of currency have been under scrutiny by the banking system, and proposals for improvement are being developed.
Research Grants
Half the net profits of the Rural Credits Department are transferred each year to the Rural Credits Development Fund. During 1975/6 grants totalling $868,000 were approved from this Fund for research, development and extension projects concerned with primary industries; grants were awarded after obtaining the advice of a Committee drawn mainly from universities and other institutions.
In 1975/6 the Bank approved grants totalling $65,000 from its Economic and Financial Research Fund for post-graduate research on economic and financial topics relevant to the Australian economy. The Bank also awarded a Fellowship and a Professorial Fellowship in Economic Policy.
Publications
The monthly Statistical Bulletin produced by the Bank contains data for which the Bank is the original source as well as a wide range of banking, financial and other economic statistics. It also includes some text describing developments in financial policy and trends in financial markets. Financial, Company and Flow of Funds Supplements to the Statistical Bulletin were also published during the year.
Premises
As foreshadowed in last year's Report, the Bank's Launceston branch closed in November 1975 and its functions were transferred elsewhere. Work is in progress on an extension to the Bank's Head Office in Sydney; completion is expected in 1978. Work has also continued on the Bank's new building in Hobart which is now expected to be completed in 1977.
Staff
The total staff of the Bank was reduced by 3 per cent over the year to 3,626 persons; this was less than 2 per cent above the level of five years earlier. Increased work pressures fell on staff at all levels and in many areas of the Bank's activities throughout 1975/6. The Board wishes to acknowledge the efficient manner in which staff members carried out their duties during an active and difficult year.
Mr A.S. Holmes currently occupies the position of Economic Consultant to the Department of Prime Minister and Cabinet. In all, 19 officers are seconded to other organisations overseas and in Australia. Since the last Annual Report was published, Messrs A.C. McPherson, Adviser to the Governor, R.A.S. Bywater, General Manager, Note Issue Department, Fitzroy, and K.W. Down, Manager, Sydney Office have retired.