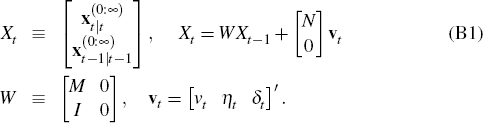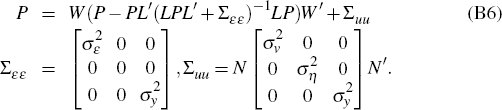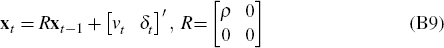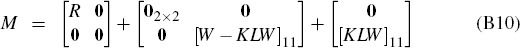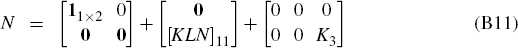RDP 2007-12: Dynamic Pricing and Imperfect Common Knowledge Appendix B: The Law of Motion of the Expectations Hierarchy
December 2007
- Download the Paper 287KB
Define a new state vector Xt as
For a given W, firm j's estimate of Xt will evolve according to the updating equation
where K is the Kalman gain matrix and St(j) is firm j's observation vector. L is a matrix that maps an expected state into an expected observation vector. They are given by
Take averages of Equation (B2) across firms and use the definitions of the observables in St to write the average updating equation as
Finally, use the definition of the hierarchy 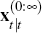 :
:
and the fact that the exogenous state xt|t follows the known process
to identify M and N:
where [·]11 is the upper left submatrix of the appropriately partitioned matrix [·].