RDP 2021-09: Is the Phillips Curve Still a Curve? Evidence from the Regions Appendix A: RBA Aggregate Wage Phillips Curve Specification, Coefficients and Implied Slope
September 2021
- Download the Paper 1,707KB
The current RBA wage Phillips curve forecasting model is specified as[46]:
where:
| Quarterly growth in the wage price index (WPI) (hourly rates excluding bonuses); seasonally adjusted. | |
| ut | Quarter-average unemployment rate; seasonally adjusted. |
| Non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment (NAIRU; described in Cusbert (2017)); two-sided smoothed quarterly estimate. | |
| Quarterly change in the unemployment rate; seasonally adjusted. | |
| Year-ended growth in the domestic final demand implicit price deflator. | |
| Trendt | Trend inflation expectations estimated using a Kalman filter (described in Cusbert 2017); two-sided smoothed quarterly estimate. |
| Dependent variable = WPI excluding bonuses | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | −0.240 (0.243) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.354*** (0.103) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| −0.476*** (0.122)(a) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| −0.151** (0.061) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.097 (0.074) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1.070*** (0.404)(a) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.73 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Notes: Standard errors in parentheses; ***, **, and * denote statistical significance at the 1, 5, and 10 per cent levels, respectively (a) The standard errors on these variables do not account for the generated regressor problem Sources: ABS; Authors' calculations |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
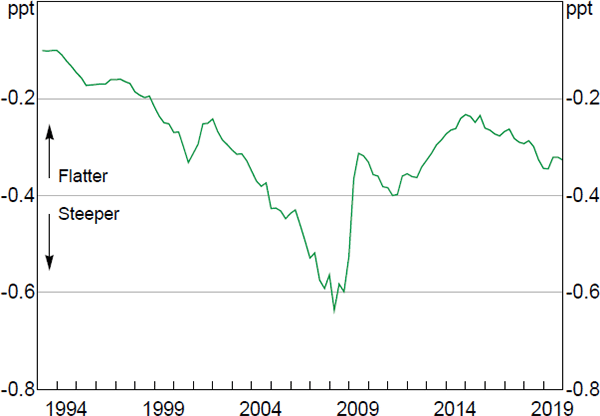
Notes: Short run; as implied by the RBA's wage Phillips curve model; uses time-varying two-sided NAIRU estimate
Sources: ABS; Authors' calculations
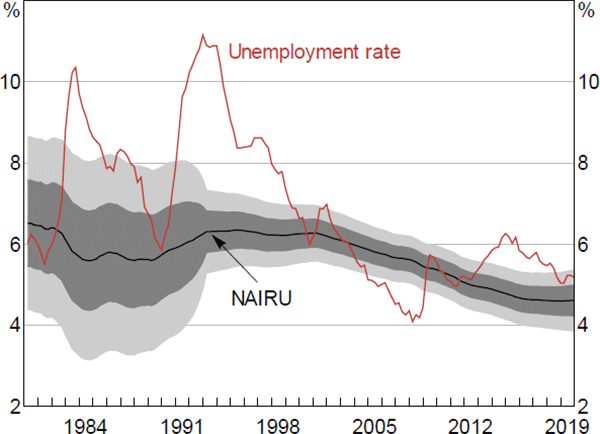
Notes: Two-sided smoothed estimates; shaded areas represent one and two standard error bands around central estimates
Sources: ABS; RBA
Footnote
Although the nonlinearity imposed by the RBA's wage Phillips curve model has not changed since Debelle and Vickery (1997), the model is periodically assessed and adjusted as part of the internal RBA forecast review process. Here we present the current model specification. [46]